
At 29 years old, my favorite compliment is being told that I look like my mom. Seeing myself in her image, like this daughter up top, makes me so proud of how far I’ve come, and so thankful for where I come from.
Research Smarter, Not Harder: 4 Research Methods Every Designer Should Use
Explore 4 UX research methods: competitive analysis, user interviews, surveys, A/B testing for design optimization.
Understanding different research methods is crucial for designers to create effective products and experiences. Research allows designers to gain insights into user behaviors, needs, motivations and pain points. This knowledge directly informs design decisions, ensuring the end result aligns with user goals.
There are four key types of research methods designers should leverage: secondary research, primary research, quantitative research and qualitative research. Each approach has distinct benefits and can reveal different types of insights. Using a combination of research techniques allows designers to gain a comprehensive understanding of the problem space and users.
This article will provide an overview of these four research methods, outlining how they work and why they are valuable for designers. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each approach enables designers to select the right research tools for their specific project goals and parameters. With the ability to gather meaningful user insights, designers can create human-centered solutions that successfully address real user needs.
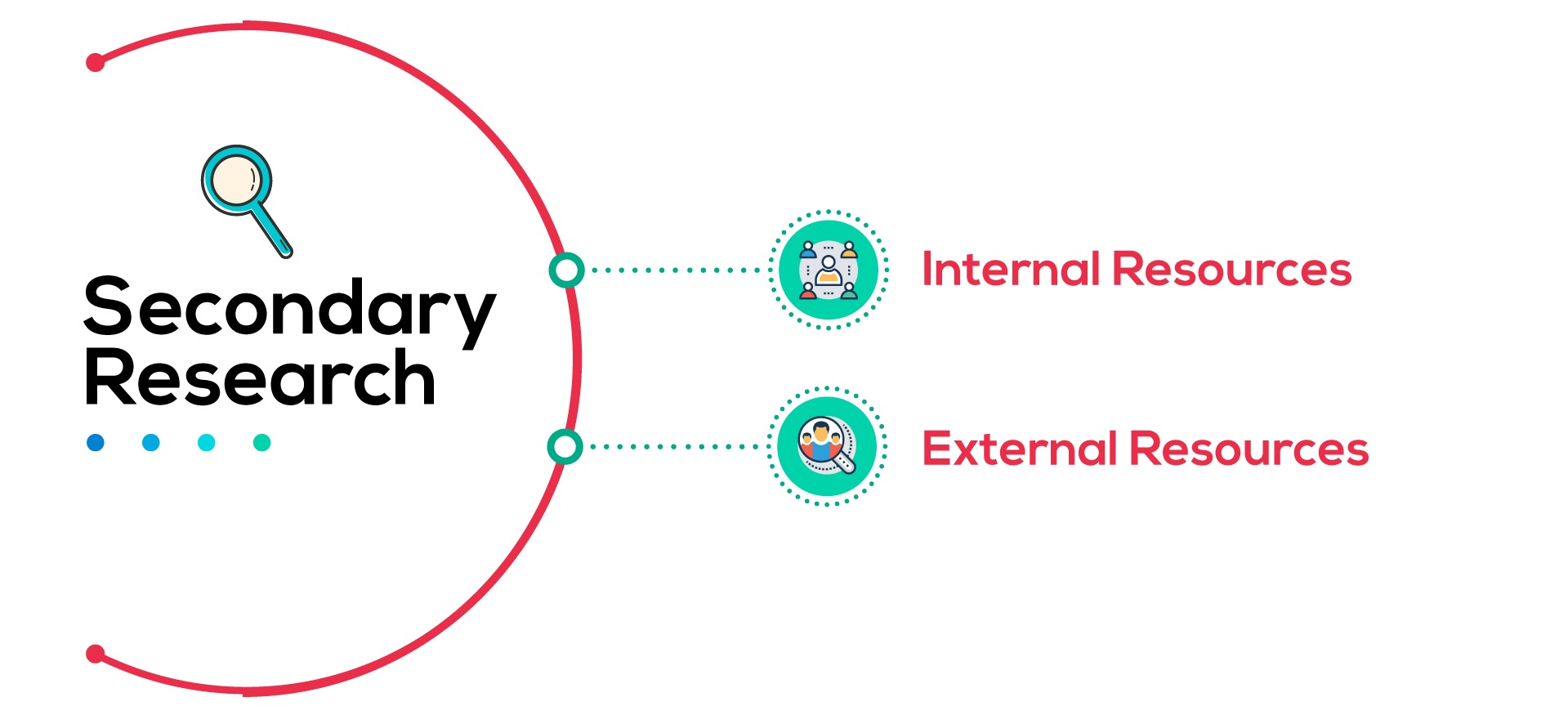
Secondary research involves using existing data and information to gain insights and understanding. It analyzes available data that has already been collected by other researchers, organizations, or sources.
Some key aspects of secondary research:
Relies on data that already exists, rather than collecting new data directly. This can include market reports, industry data, demographic statistics, government data, and more.
Involves reviewing, summarizing, and analyzing existing materials. The researcher examines, interprets, and draws conclusions from pre-existing information.
Less time-consuming and lower cost compared to primary research. The data has already been gathered, so it avoids the lengthy process of collecting new data.
Provides a solid background understanding of the research topic or question at hand. Looking at existing data lays the foundation before conducting any primary research.
Helps determine if primary research is needed and identify gaps. Secondary research reveals what is already known and highlights areas that require additional original research.
Sources include libraries, databases, journals, surveys, studies, reports, and more. Both offline and online sources can be leveraged.
Overall, secondary research is an efficient and cost-effective way to gain a strong understanding of a topic by analyzing existing information and data. It serves as an important first step in the research process. While it has limitations in providing original insights, it sets the stage for primary research by identifying gaps and guiding the focus.
Primary research involves gathering new data first-hand rather than relying on already existing sources. It focuses on proprietary information relevant to the specific project at hand. Primary research can take considerable time and resources, but provides insights tailored to the current needs.
Some examples of primary research methods include:
Surveys - Questionnaires distributed to a sample of the target user group. Provides quantitative data on user preferences, habits, etc.
Interviews - One-on-one discussions with users about their experiences, perceptions, and needs. Provides in-depth qualitative data.
Focus groups - Facilitated discussions with a small group of users. Provides qualitative data on user opinions.
User testing - Observing users interacting with a product to identify usability issues. Provides qualitative insights on user behavior.
Ethnographic research - Studying users in their natural environments to understand cultural influences. Immersive qualitative data.
The key advantage of primary research is it generates new data specific to the design problem at hand, rather than relying on pre-existing data. It may uncover user needs and insights that are not addressed in secondary sources. The tradeoff is primary research requires hands-on effort and is more resource intensive than relying on secondary data. But for critical projects, the proprietary insights make primary research invaluable.
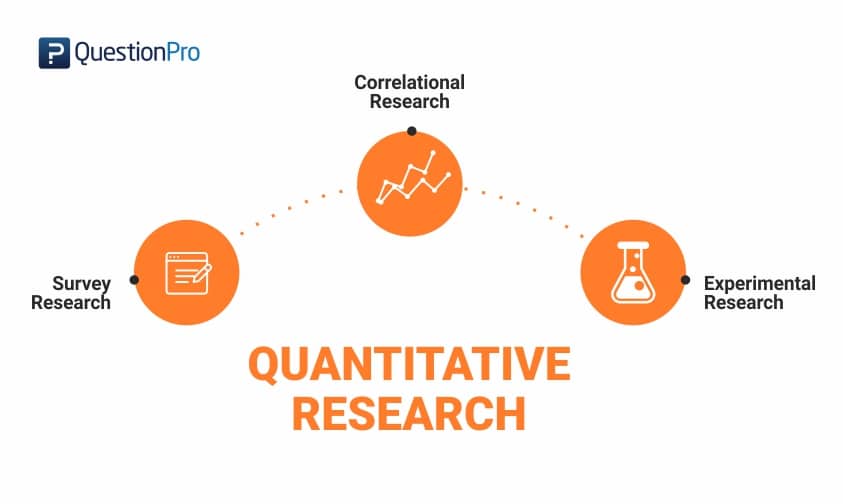
Quantitative research focuses on numerical data and hard facts. It relies on surveys, polls, questionnaires, etc. to collect measurable, quantifiable insights.
This type of research aims to quantify behaviors, opinions, trends, and other variables within a target population. It emphasizes objective measurements and statistical analysis rather than subjective perspectives.
Some examples of quantitative methods include:
Surveys - Gathering input through structured questionnaires with closed-ended questions. Researchers can survey a sample population and generalize findings to a larger group.
Online polls - Quick online questionnaires to gauge initial reactions. Provides fast quantitative data but from a smaller sample.
Sales data tracking - Analyzing numerical sales data to identify trends and patterns. Useful for understanding consumer behavior.
Website analytics - Collecting metrics like page views, bounce rates, etc. Provides quantifiable data on site usage.
Social media monitoring - Tracking measurable stats like likes, shares, followers, etc. Shows quantifiable engagement.
The main benefits of quantitative research are:
The drawbacks are that it may miss subjective insights like emotions, motivations, etc. But it remains an indispensable method for designers to understand user behaviors, preferences, and trends. The quantifiable insights complement and strengthen qualitative research.
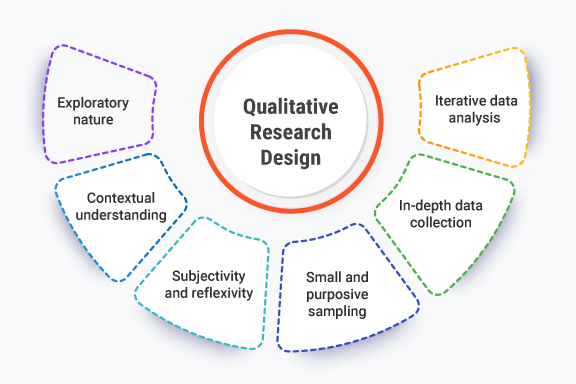
Qualitative research focuses on non-numerical data like interviews, focus groups, and observation. It aims to provide an in-depth understanding of human behaviors, motivations, and opinions.
Unlike quantitative research that uses surveys and statistics, qualitative methods allow designers to explore the human side of problems. This type of research is especially useful for understanding why users think and feel the way they do.
Some common qualitative techniques include:
Interviews: One-on-one conversations that let designers probe deep into thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Interviews can be structured or unstructured.
Focus groups: Facilitated group discussions that uncover perspectives from multiple users at once. Group dynamics often reveal insights that individual interviews do not.
Observation: Watching users interact in their natural environment provides authentic insights into behaviors and pain points. This could include observing someone use a website or prototype.
User diaries/journals: Getting users to record thoughts over time reveals patterns and contextual information. Diaries capture real-world behaviors rather than just opinions.
Qualitative data is highly descriptive and captures important context about the human experience. While sample sizes are smaller than quantitative studies, the depth of insight can be invaluable for truly understanding user needs and emotions. Qualitative research allows designers to build empathy, uncover problems, and identify opportunities through the eyes of real users.
Usability testing involves directly testing products or services with target users to identify usability issues and problems. This type of primary research is critical for designers to understand how real users interact with their designs.
Some key methods of usability testing include:
Moderated tests - These involve having test users complete tasks while being observed by a researcher. The researcher can ask questions and gain insights into the user's thought process.
Unmoderated tests - Users complete tasks on their own, while their interactions are recorded. This provides natural behavior data without researcher involvement.
A/B testing - Two versions of a design are compared by showing them to different user groups. This identifies which version performs better based on key metrics.
Usability testing provides empirical data directly from users about how they use and interact with designs. It can uncover issues that may not be anticipated by designers. Testing early and often is crucial for creating usable products and services.
Competitive analysis is a key research method that all designers should utilize. This involves thoroughly analyzing your competitors and their offerings. The goal is to identify the strengths and weaknesses of other products and services in your market so you can apply those learnings to your own designs.
When conducting a competitive analysis, you'll want to review your competitors' products, marketing materials, websites, patents, social media, pricing, and more. Gather as much information as possible to understand their positioning, messaging, features, user experience, visual identity and branding.
Analyze what your competitors are doing well and what shortcomings they have. Look for gaps or opportunities in the market that your own designs could fill. Examine the language competitors use to describe their offerings as this often reveals how they position themselves. Also pay close attention to user feedback on forums and reviews to identify pain points.
An effective competitive analysis will reveal valuable insights to help differentiate your designs. You may find inspiration for features to include or flaws to avoid based on competitors' successes and failures. Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial context that will enable you to craft designs that stand out in your industry. Competitive research should inform your work throughout the design process, from ideation to final execution.

User personas are fictional representations of your target users that help inform design decisions. They outline demographic, psychographic, and behavioral details about various user segments. Creating detailed and realistic personas for each of your core target audiences allows designers to ensure their work meets real user needs.
When developing user personas, aim to define the following elements:
With well-defined user personas, designers can make decisions through the lens of different target users. When ideating and prototyping, ask "Would this persona understand how to use this feature?" and "Does this design resonate with the persona's values?"
Keeping user personas in mind ensures the end product connects with and delights real people. The more designers know about their target users, the better they can craft experiences that fit seamlessly into their lives.

Focus groups are a form of qualitative research that involve facilitated discussion with a small group of users, typically 6-12 people. The moderator leads the group through a series of questions designed to gain insights into their attitudes, perceptions, opinions, beliefs, motivations and feelings about a product, concept, advertisement etc.
Focus groups require careful planning and experienced moderation. The moderator must create a permissive, non-threatening environment that encourages participants to share their thoughts openly. Questions are usually open-ended to spark discussion between participants.
The group dynamic helps focus groups uncover information that may be missed in individual interviews. Listening to others verbalize their thoughts can stimulate ideas and discussion. Participants can respond to and build upon the responses of others in the group.
However, the group setting also has disadvantages. The open nature makes focus groups prone to going off topic. Some participants may be hesitant to share controversial opinions or sensitive information amongst strangers. The small sample size makes it difficult to generalize findings to the broader population.
Overall, focus groups provide qualitative insights that quantitative methods may overlook. They can help generate ideas, screen concepts, diagnose potential issues, and reveal consumer attitudes. When combined with other methods, focus groups can be a valuable part of the design research process.

When designing any product or service, research is a crucial first step. There are many different research methods available, each with their own strengths and weaknesses. By using a combination of both primary and secondary research, quantitative and qualitative methods, designers can gain a comprehensive understanding of the problem space and user needs.
Some key points about the different research methods discussed:
Secondary research involves gathering existing data and information. It provides background context and helps define the scope of the design problem. Sources like published reports, academic studies, and news articles can uncover useful insights.
Primary research collects new data directly from users. Surveys, interviews, focus groups, and usability testing produce original user feedback. However, it can be more time-consuming than secondary research.
Quantitative research emphasizes numerical data and statistical analysis. Surveys with closed-ended questions generate quantifiable data to reveal trends and patterns. But the data lacks qualitative depth.
Qualitative research explores subjective insights through open-ended questions. Interviews and observations produce rich, descriptive data about user behaviors, motivations, and perceptions.
Usability testing evaluates a product by observing real users interact with it. This reveals usability issues and opportunities to improve the user experience. Testing with a small set of users can uncover the majority of problems.
Competitive analysis examines existing products and solutions in the market. This can inspire and inform better design decisions. However, don't just copy competitors. Strive for innovation.
The most effective research combines these methods to gain both qualitative insights and quantitative data. Well-rounded research leads to a deeper understanding of the target users and their needs. This understanding ultimately enables designers to create better products that solve real problems for real people. The goal of research is to eliminate assumptions and ground designs in evidence and user-driven insights. This foundation leads to more successful, useful, and innovative designs.
Jone Doe
Duis hendrerit velit scelerisque felis tempus, id porta libero venenatis. Nulla facilisi. Phasellus viverra magna commodo dui lacinia tempus. Donec malesuada nunc non dui posuere, fringilla vestibulum urna mollis. Integer condimentum ac sapien quis maximus.
Fatima Jane
Duis hendrerit velit scelerisque felis tempus, id porta libero venenatis. Nulla facilisi. Phasellus viverra magna commodo dui lacinia tempus. Donec malesuada nunc non dui posuere, fringilla vestibulum urna mollis. Integer condimentum ac sapien quis maximus.
Jone Doe
Duis hendrerit velit scelerisque felis tempus, id porta libero venenatis. Nulla facilisi. Phasellus viverra magna commodo dui lacinia tempus. Donec malesuada nunc non dui posuere, fringilla vestibulum urna mollis. Integer condimentum ac sapien quis maximus.